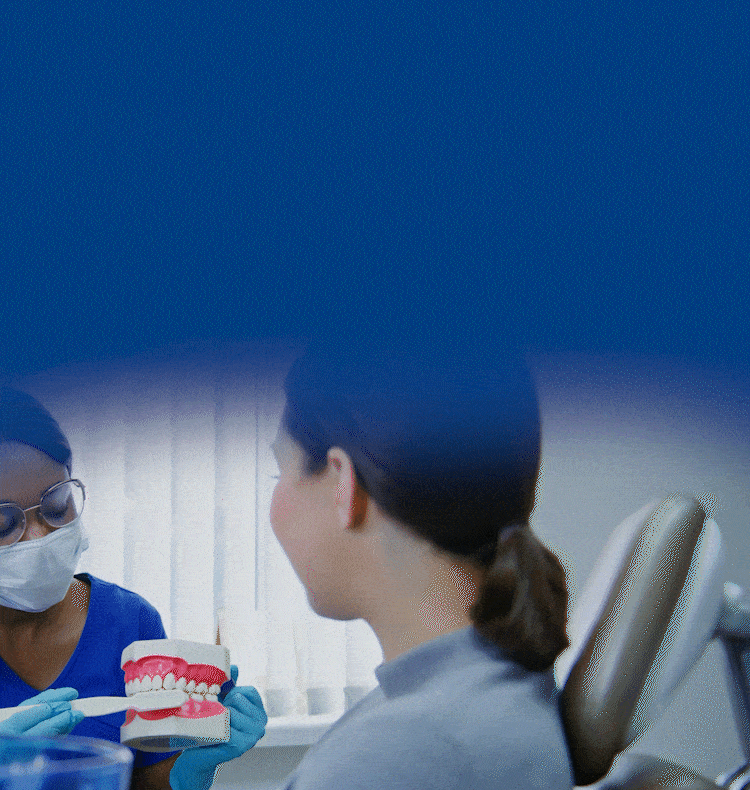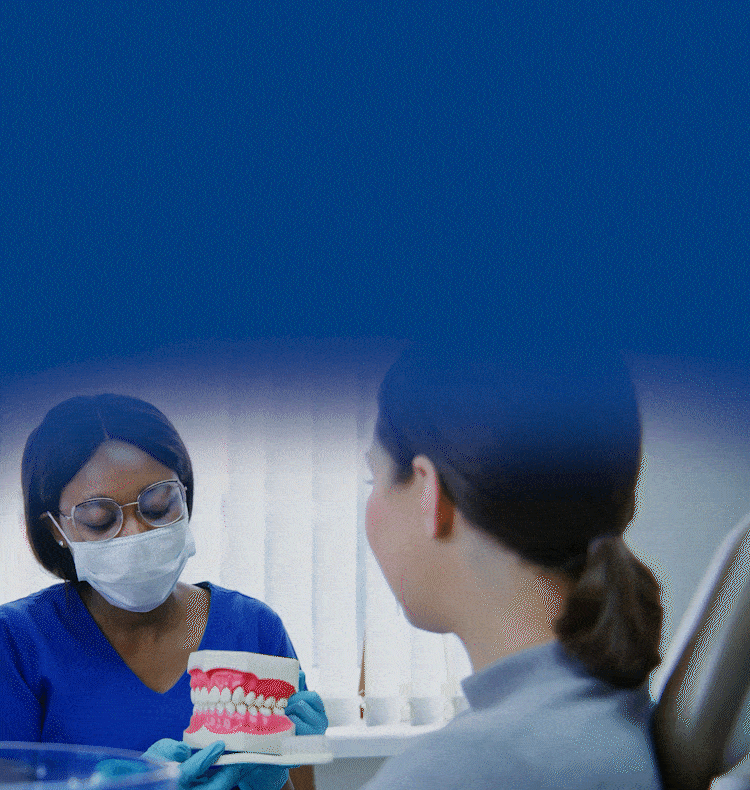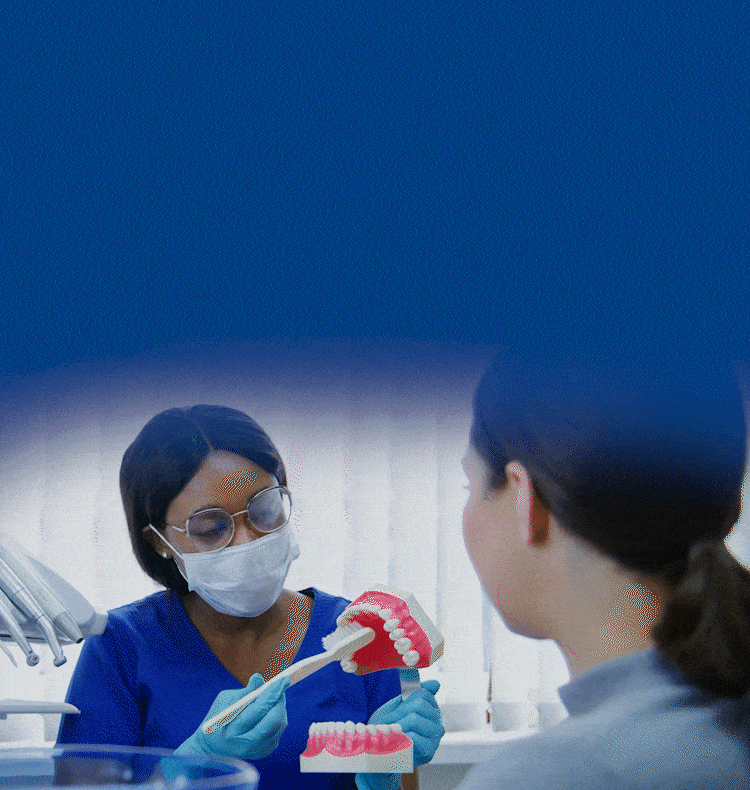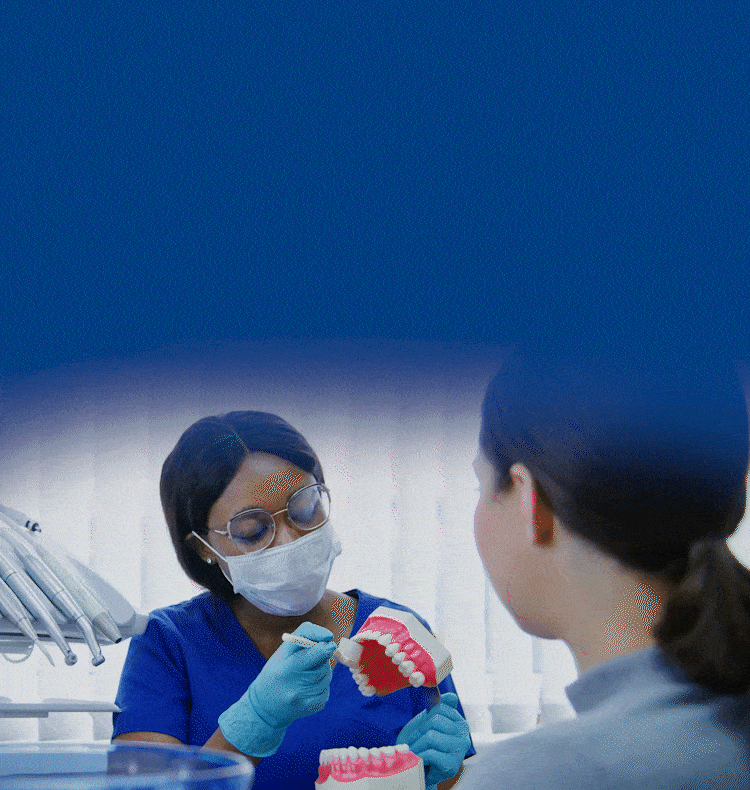
TOGETHER WE CAN BUILD HEALTHIER & BRIGHTER SMILES
150+ FREE Continuing Education Courses
Featured Courses
Scroll to Item 1
Scroll to Item 2
Scroll to Item 3
Interested in Crest + Oral-B Products?
Scroll to Item 1
Scroll to Item 2
Scroll to Item 3
Scroll to Item 4
Crest Pro-Health Gum Detoxify
Order NowCrest Kids Color Changing Toothpaste
Order NowCrest Pro-Health Gum Detoxify Toothpaste Sample Size
Order NowClinically Proven Healthier Gums
Learn MoreScroll to Item 1
Scroll to Item 2
Scroll to Item 3
Scroll to Item 4
Professional Resources
Oral-B iO - Why recommend oscillating rotating technology?
Learn MoreWhole Body Health
Learn More#Hygienist Proud - Resources for you!
Learn MoreScroll to Item 1
Scroll to Item 2
Scroll to Item 3
Student & Faculty Quick Links
Enter Assignment Number
Use the Assignment Number provided to find the course
Create assignments with a wide range of courses available
Review the submitted Assignments
Case studies for students and professionals
Interactive learnings for you



